Lifting Electromagnet
Crane magnets,Lifting Electromagnet
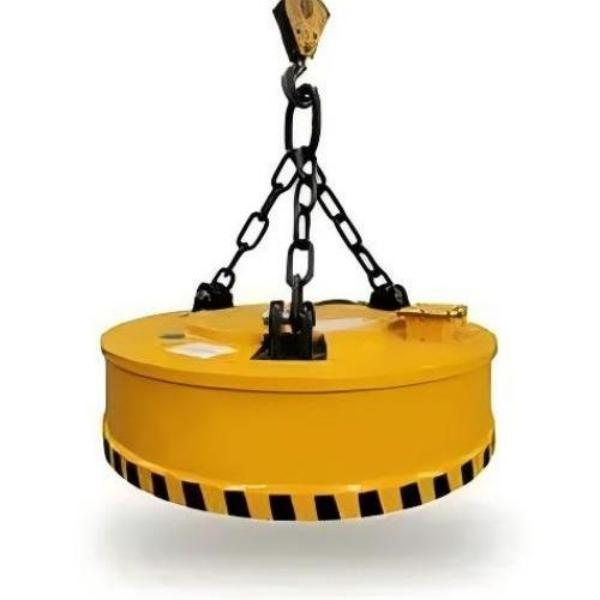
- MW5 Series – Scrap Steel Lifting Electromagnet
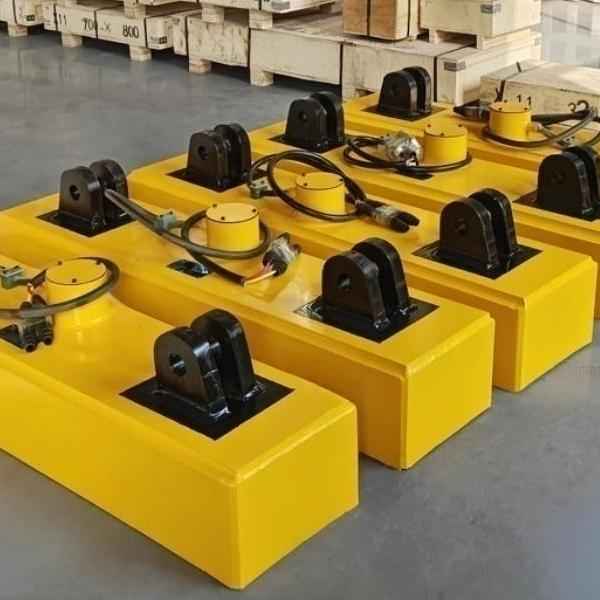
- MW12 Series – Rectangular Electromagnetic Chuck for Bundled Rebar
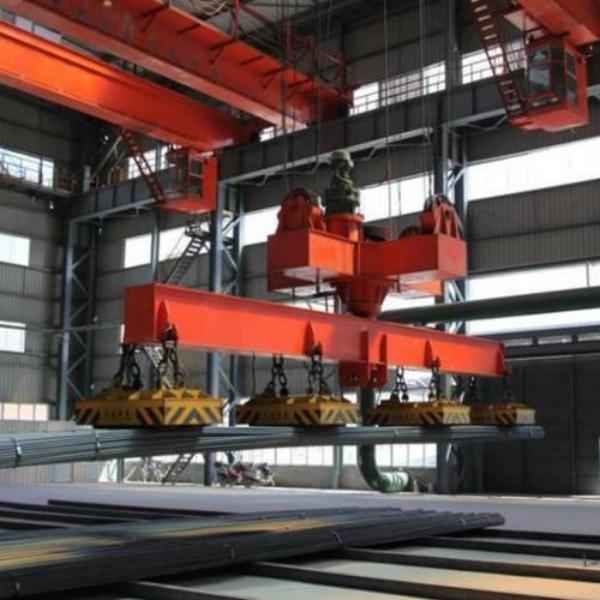
- MW22 Series – Steel Ingots and Large Blooms
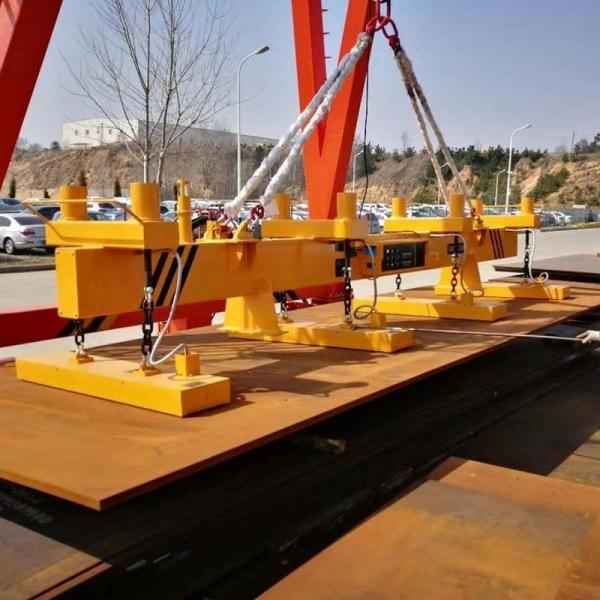
- MW84 Series – Electromagnet for Medium and Thick Steel Plates
Overview of Lifting Electromagnet
A lifting electromagnet is a device that generates a magnetic field when electric current passes through a coil. This magnetic field enables it to lift ferromagnetic materials, and the magnetism disappears when the current is turned off. Widely used in industries such as metallurgy, mining, machinery, and transportation, lifting electromagnets offer an efficient and safe solution for material handling, particularly in applications that require frequent lifting and moving of heavy loads.
Lifting Electromagnet Key Features
- Simple Control: The magnetism of the lifting electromagnet is controlled by simply switching the current on or off, making it easy to activate or deactivate the magnetic force when needed.
- Flexible Adjustment: By adjusting the intensity and direction of the current, the strength and polarity of the magnetic field can be modified to suit specific requirements, providing high flexibility.
- Wide Applications: Lifting electromagnets are suitable for industries such as metallurgy, machinery, mining, and transportation, where they are used to lift ferromagnetic materials like steel.
Applications
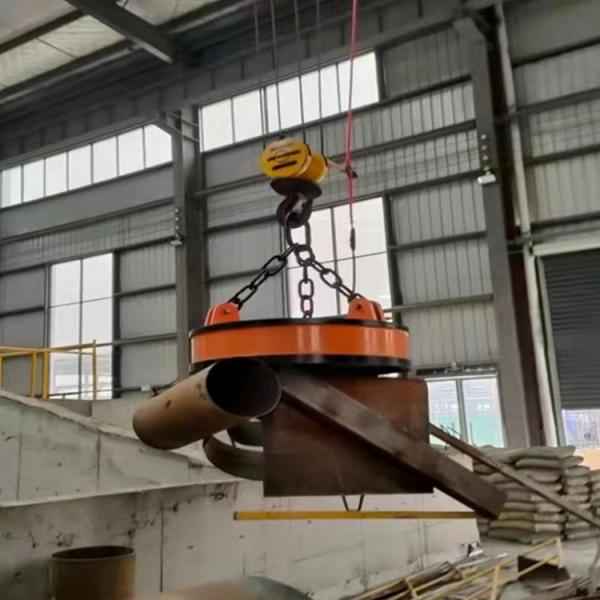
- Metallurgy and Mining: Lifting electromagnets are used to lift steel, cast iron ingots, and other magnetic materials, playing a vital role in steel production and mineral handling.
- Machinery and Manufacturing: They are widely used to lift machinery parts, metal scrap, and other materials, improving efficiency in manufacturing plants and production lines.
- Transportation: In industries such as railways, ports, and shipbuilding, lifting electromagnets replace manual labor, facilitating the lifting of heavy loads and saving both time and manpower.
- Special Environments: Lifting electromagnets are capable of operating in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, underwater, dusty environments, or areas with toxic gases, ensuring reliable performance under challenging circumstances.
Specialized Models
- MW5 Series – Scrap Steel Lifting Electromagnet: Designed for lifting scrap steel, cast iron ingots, steel balls, and other scrap materials.
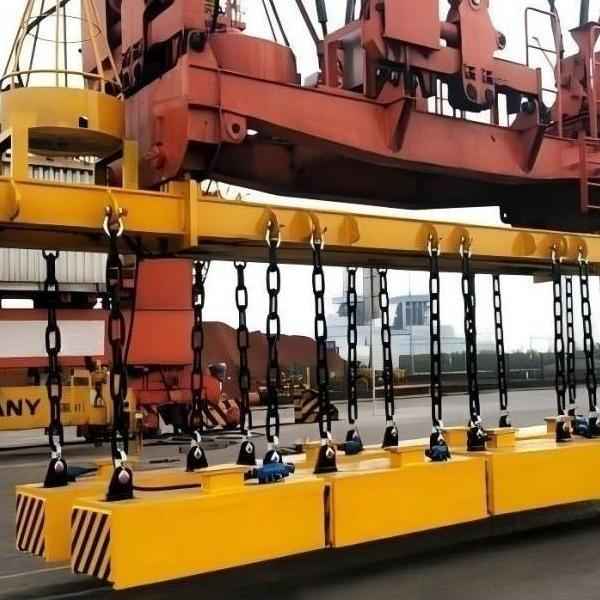
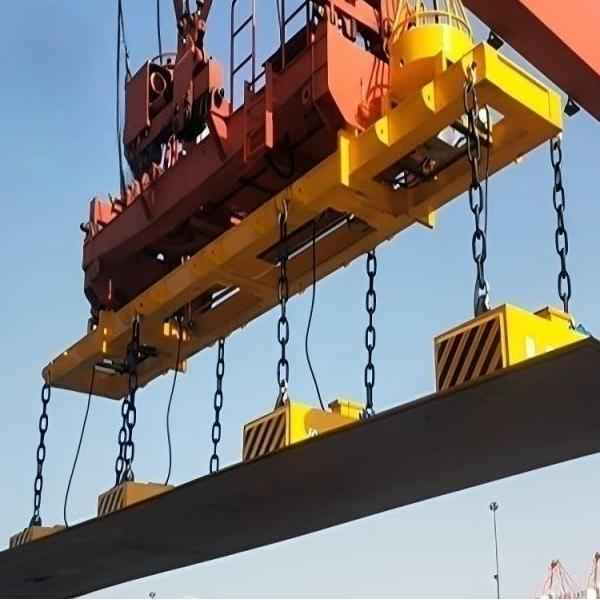
- MW12 Series – Rectangular Electromagnet: Ideal for lifting bundled rebar, featuring a high-permeability magnetic circuit capable of penetrating multiple air gaps.
- MW22 Series – Steel Ingots and Large Blooms: Optimized for lifting steel ingots, large initial blooms, and structural steel components.
- MW84 Series – Electromagnet for Medium and Thick Steel Plates: Specially designed for lifting steel plates with thicknesses ranging from 6 to 32 mm, ensuring safe and accurate operations. For longer plates, multiple electromagnets should be used together.
Advantages
- Efficient and Reliable: Lifting electromagnets provide quick and stable lifting capabilities, greatly improving operational efficiency.
- Energy-Efficient: They consume less energy while meeting lifting requirements, making them an environmentally friendly option.
- High Safety: With high-quality materials and advanced design, lifting electromagnets come equipped with safety features that prevent accidental drops of materials.
- Strong Adaptability: They are capable of operating in various environments, including high temperatures, humid conditions, dusty areas, and toxic environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lifting electromagnets are indispensable in industrial applications, offering a simple, efficient, and safe method for material handling. Whether used in steel production, mineral handling, machinery manufacturing, or under extreme conditions, lifting electromagnets ensure reliable, safe, and efficient lifting operations. Their ease of use, energy efficiency, and ability to adapt to different environments make them invaluable tools for industries requiring heavy lifting and material movement.