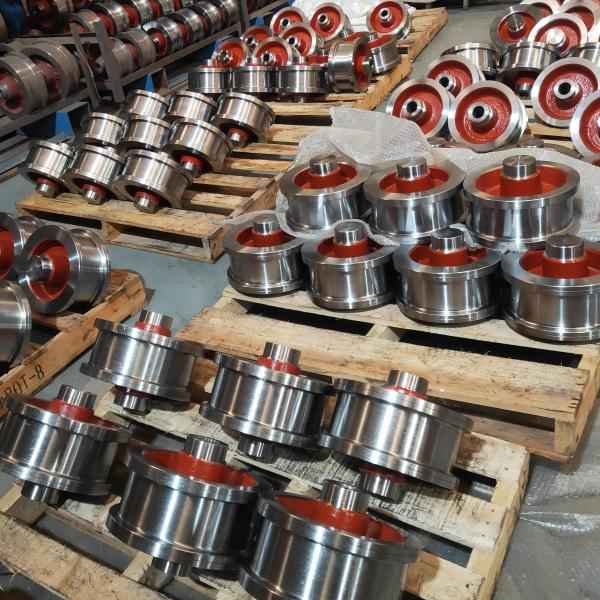
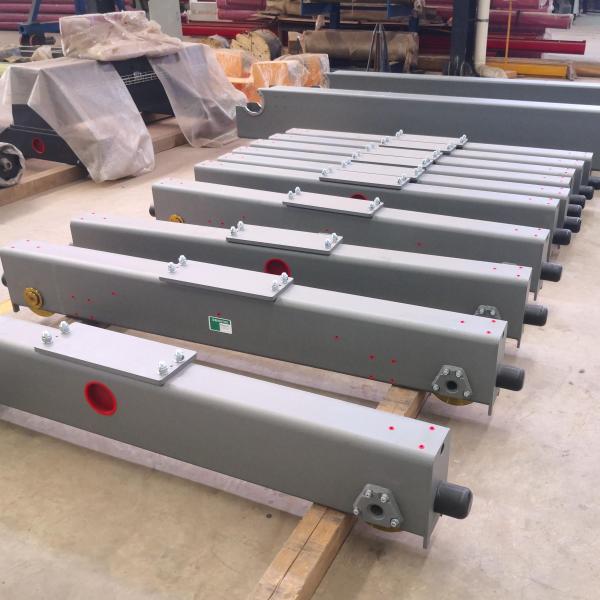
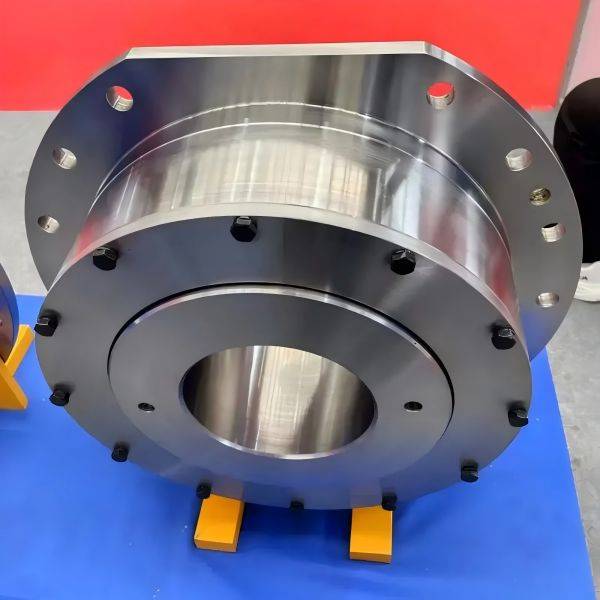
Materials of Crane Wheels
The material selection for crane wheels depends on factors such as the working environment, load capacity, and wear resistance. Below are the most commonly used materials:
1. Carbon Steel
- Common Grades: 45# steel
- Key Features:
- Offers moderate strength and easy machinability.
- Manufacturers often use it for medium-duty cranes.
- To enhance wear resistance, they usually apply surface hardening treatments.
2. Alloy Steel
- Common Grades: 42CrMo, 65Mn
- Key Features:
- Provides high strength and excellent wear resistance.
- Engineers prefer it for heavy loads, high speeds, and impact-intensive applications.
- They typically perform heat treatment (such as quenching and tempering) to improve hardness and fatigue resistance.
3. Cast Steel
- Common Grades: ZG50SiMn, ZG430-640, ZG40Cr
- Key Features:
- Works well for extreme loads and harsh environments.
- Offers superior impact resistance and crack prevention.
- Foundries can customize alloy compositions to meet specific needs.
4. Ductile Iron
- Common Grades: QT500, QT700
- Key Features:
- Absorbs impact forces efficiently and provides good wear resistance.
- Engineers often use it for medium-load applications.
- While it costs less, it cannot handle as much weight as alloy steel.
5. Stainless Steel
- Common Grades: 304, 316L
- Key Features:
- Performs well in corrosive environments, such as chemical plants and offshore platforms.
- Has lower strength compared to alloy steel, so it suits light-duty cranes.
- Due to its high cost, companies use it only when corrosion resistance is critical.
Crane Wheels Surface Treatments
To extend the lifespan of crane wheels, manufacturers apply various surface treatments:
- Induction Hardening: Increases surface hardness, typically reaching HRC 50-60.
- Nitriding Treatment: Enhances wear and corrosion resistance.
- Thermal Spraying: Improves surface durability and abrasion resistance.
Each material and treatment method serves a different working condition. Therefore, engineers should select the most suitable option based on the specific operational requirements of the crane.