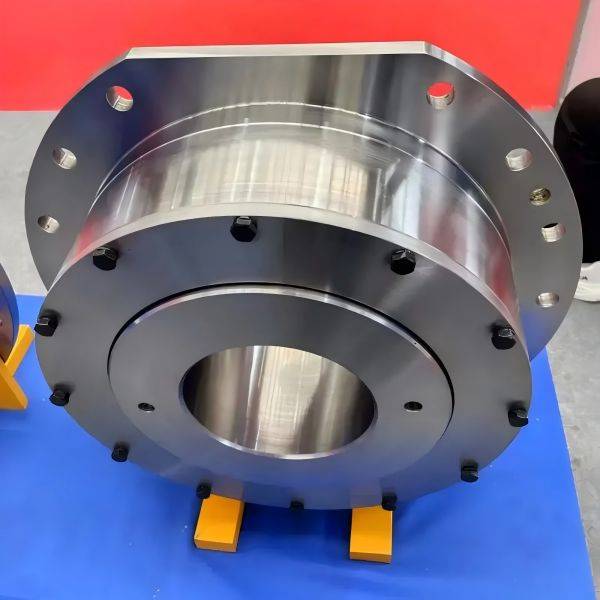
Introduction to Overhead Crane Wheel
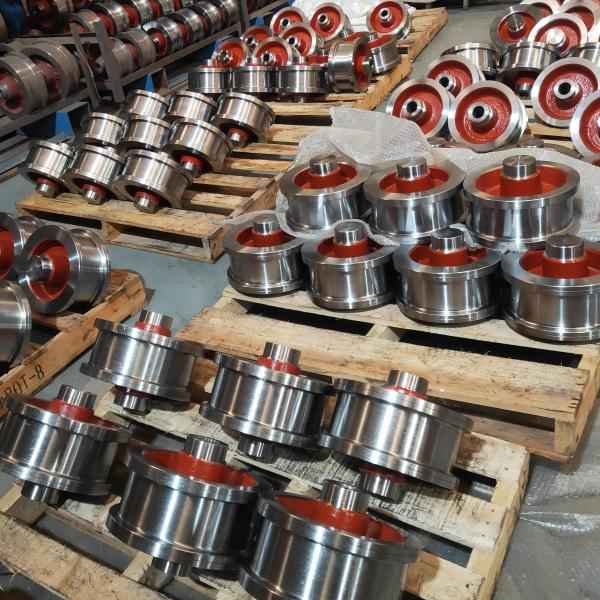
Overhead crane wheels are essential components of the crane’s traveling mechanism. They primarily support the crane body and enable it to move along the track, facilitating material handling and loading. Their performance directly impacts the crane’s operational efficiency, safety, and lifespan.
Classification of Crane Wheel
Overhead crane wheels typically fall into two categories: drive wheels and idle wheels.
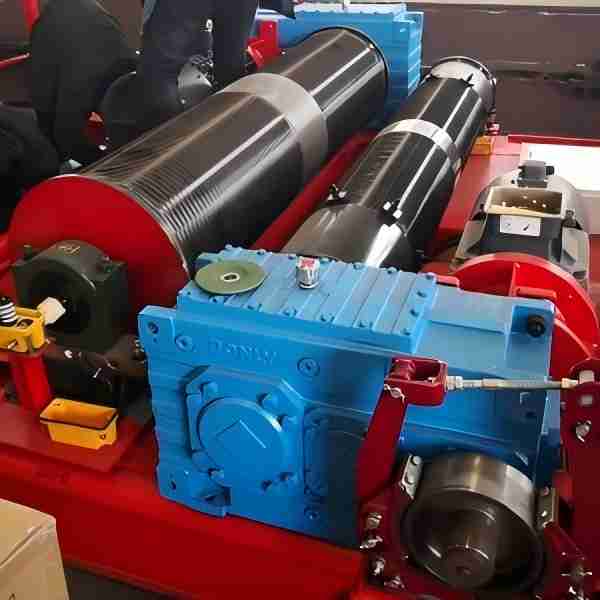
- Drive Wheels: These wheels connect to the crane’s drive system. The motor powers them through a reducer, enabling the crane to move along the track.
- Idle Wheels: These wheels do not have a driving function. Instead, they bear the crane’s weight and roll along the track passively.
Based on material composition, crane wheels can be classified into forged steel wheels, cast steel wheels, and composite wheels. Among these, forged steel wheels are the most widely used in heavy-duty cranes due to their high strength and wear resistance.
Key Features of Crane Wheel
- High Strength and Wear Resistance: Since overhead crane wheels endure significant loads and frequent operational impacts, manufacturers use high-strength alloy steel. Additionally, they apply quenching treatments to enhance durability.
- Precision Manufacturing and Processing: Crane wheels require high manufacturing precision, particularly regarding rim and tread concentricity and hardness distribution. These factors ensure smooth operation, reduce uneven wear, and minimize track damage.
- Corrosion and Fatigue Resistance: In humid or corrosive environments, crane wheels require special anti-corrosion treatments, such as surface coatings or hot-dip galvanization, to extend their lifespan.
Common Issues and Solutions for Overhead Crane Wheels
- Wheel Wear: Over time, wheel treads may wear down, leading to unstable operation. Regularly replacing or repairing wheel treads can resolve this issue.
- Rim Damage: Strong impacts or prolonged overloading can cause rim breakage, affecting normal movement. Inspecting rims periodically and replacing damaged wheels can prevent failures.
- Rail Misalignment (Rail Gnawing): If the wheels and rails are not properly aligned, the wheels may grind against the rails, leading to excessive wear. Adjusting wheel spacing or replacing severely worn wheels can help.
- Bearing Failure: A lack of lubrication or excessive load on bearings can cause operational issues or complete failure. Regularly checking lubrication levels and replacing bearings when necessary will ensure smooth performance.
Maintenance and Care of Overhead Crane Wheels
To ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of overhead crane wheels, the following maintenance practices should be implemented:
- Regular Inspections: Technicians should frequently check wheel treads, rims, bearings, and connection components. Any abnormalities must be addressed promptly.
- Proper Lubrication: Applying lubrication oil to the wheel bearings regularly will reduce friction and improve operational efficiency.
- Rail Alignment Adjustments: Maintaining the straightness of crane tracks will prevent uneven wheel wear and eliminate rail gnawing.
- Load Control: Avoiding prolonged overloading will reduce fatigue damage to the wheels and related components.
Conclusion
Overhead crane wheels serve as crucial components in crane operations. Their quality and performance directly influence the crane’s stability and safety. Proper design, correct installation, and routine maintenance can significantly extend their lifespan, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance productivity. Therefore, when selecting and using crane wheels, it is essential to consider material composition, processing techniques, and the working environment to ensure efficient crane operations.